Exotropia can be present at birth or occur later in life It can usually be managed or treated, but treatment will vary based on type and severity In some cases, the condition goes away on its own Types of exotropia Each type of exotropia can have different causes and levels of severity Intermittent exotropiaFeeling sick or having a fever may cause the intermittent exotropia to temporarily occur more frequently See your ophthalmologist as often as recommended, in order to keep the visual system finetuned with the appropriate glasses Otherwise, the progression of intermittent exotropia is not something that we can predictably controlIntermittent exotropia is an exodeviation intermittently controlled by fusional mechanisms Unlike a pure phoria, intermittent exotropia spontaneously breaks down into a manifest exotropia Prevalence Exodeviations are much more common in latent or intermittent form than are esodeviations
Strabismus Baby Symptoms Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis
Monocular exotropia causes
Monocular exotropia causes-Another name for amblyopia is lazy eye Sometimes lazy eye is present first, and it causes strabismus In most children with strabismus, the cause is unknown In more than one half of these cases, the problem is present at or shortly after birth This is called congenital strabismusUntreated exotropia can cause permanent damage to eyes Besides being anaesthetic, it can lead to partial or complete loss of vision Complications also include amblyopia or damage to the eye muscles Surgical correction may have complications such as uncontrolled bleeding, postsurgical infection, delayed healing, swelling etc
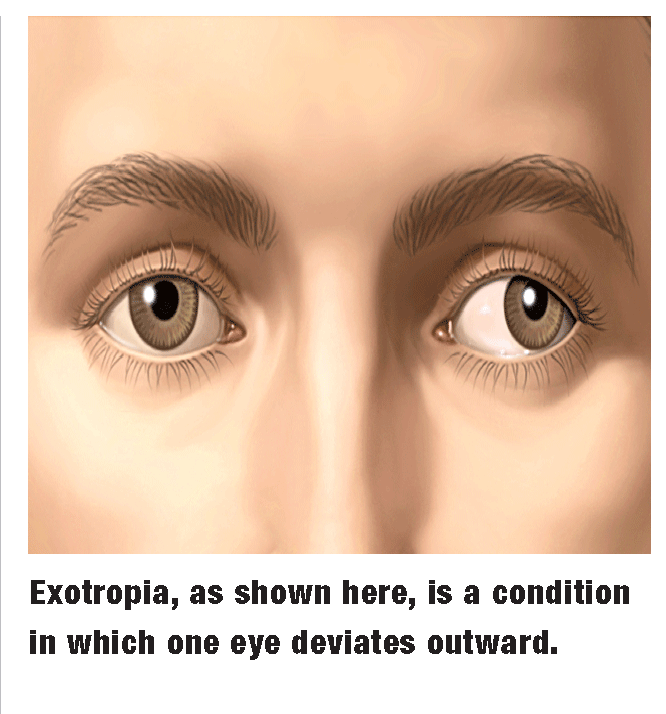



Do You See A Pattern
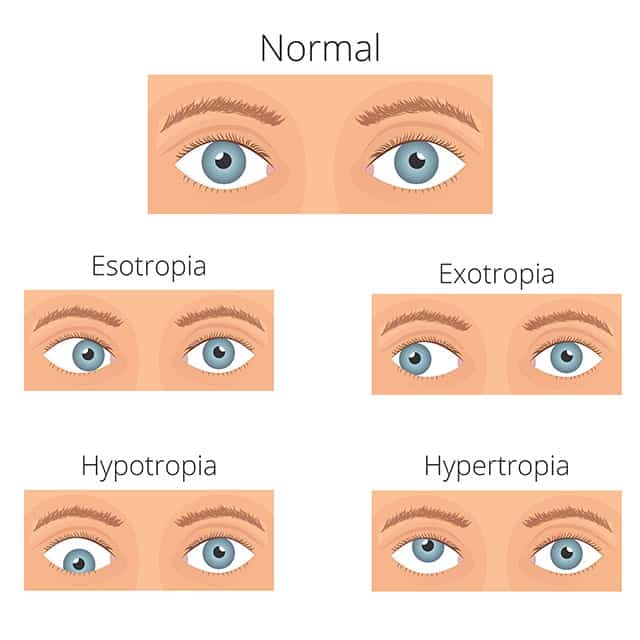
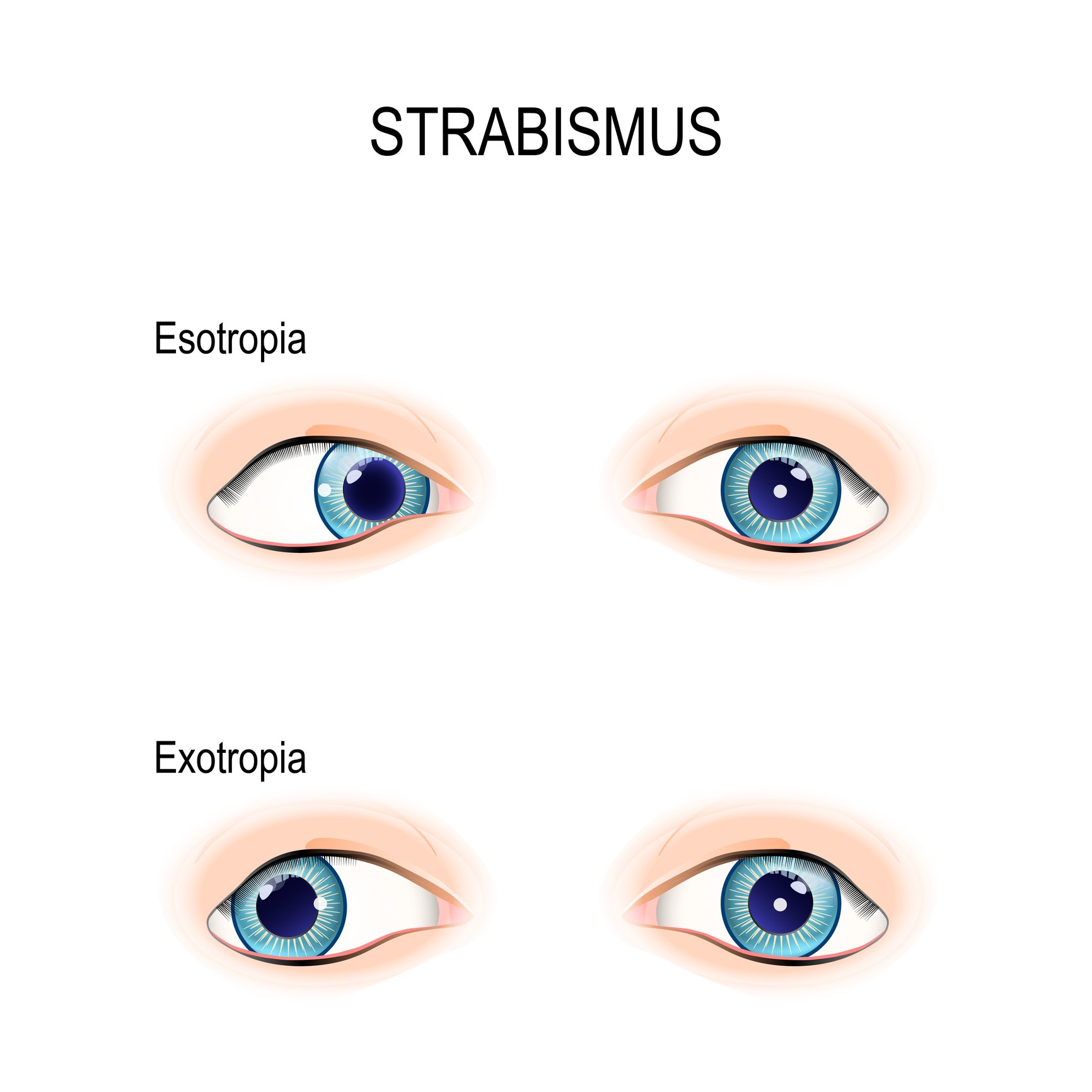
Exotropia is a common form of strabismus characterized by an outward eye turn, away from the nose Exotropia is a eye turn where one eye points outwards, this may be noticed while the child is looking at distance objects, near objects or bothExotropia is the opposite of esotropia (also known as crossed eyes) Convergence insufficiency is not as serious as exotropia With CI, your eyes may have difficulty working together when observing closeby objects But, with exotropia, your eyes may always turn outward What Causes Convergence Insufficiency?An exotropia is an outward eye turn that can have a large variety of presentations It can be intermittent, constant, unilateral, alternating and vary in magnitude An exotropia has a variety of causes, some of which can be life threatening If an eyeturn is suspected or there is a family history of an eyeturn a comprehensive eyeexamination
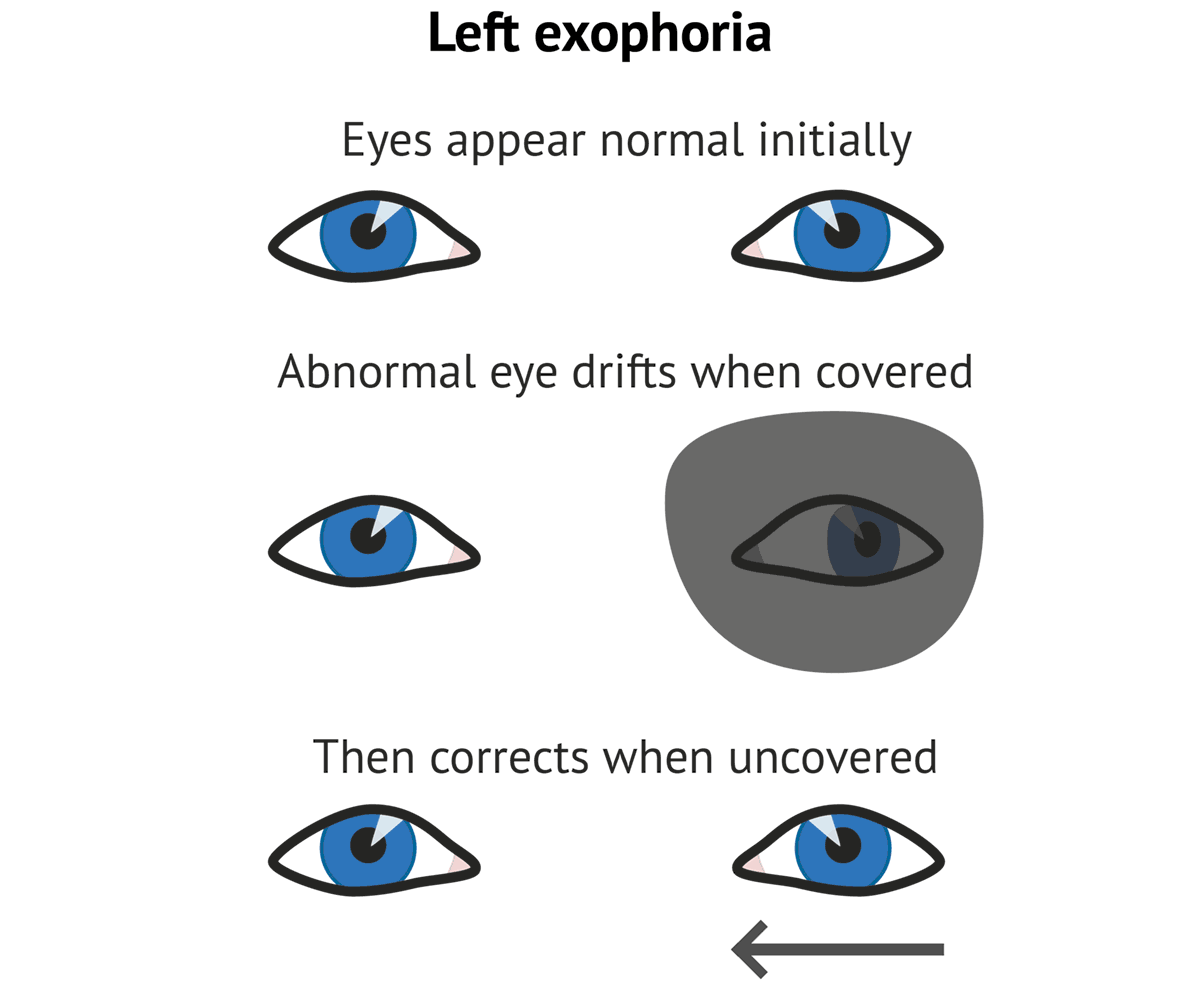
Exotropia Exotropia causes your eyes to drift outward like exophoria With exotropia, the drifting happens more often and more noticeably Untreated exophoria often intensifies into exotropiaEsophoria, like exophoria, is a condition that causes one eye to turn when covered The difference between the two conditions involves the direction in which the eye drifts or turns Esophoria causes an inward eye turn, as the eye drifts toward the nose Esophoria usually occurs due to over stimulation of the focusing lens during close visionSimilarly, Vexotropia may be confused with divergence excess type of exotropia Measurement of deviation in the 3 sets of gaze will reveal the true pattern Measurement of deviation in 9 gazes Overelevation or overdepression in
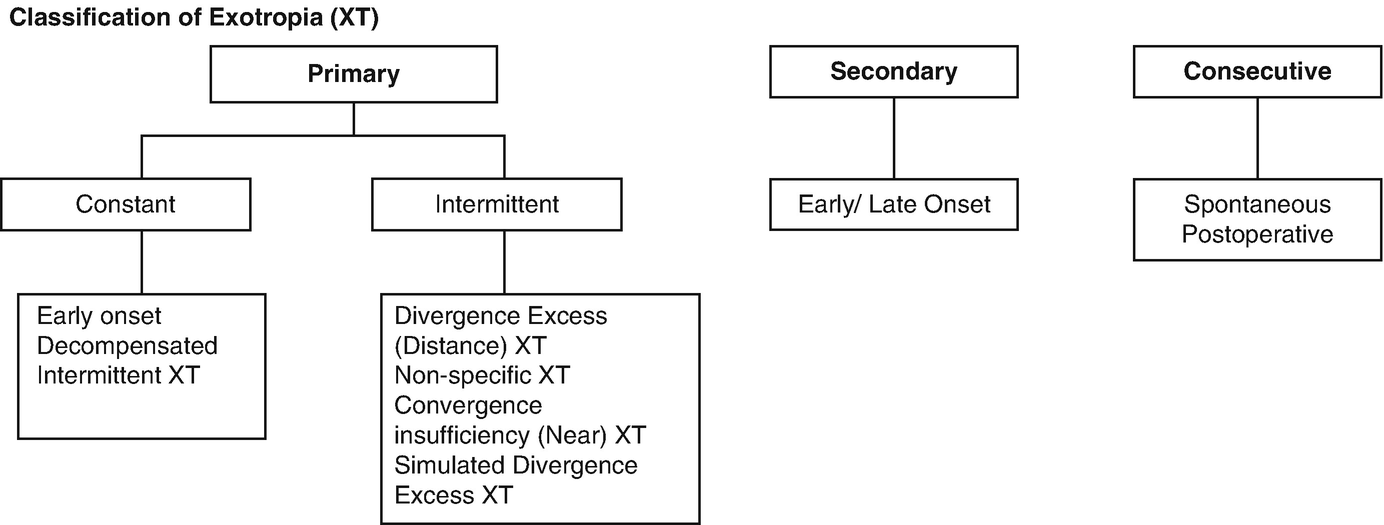
Intermittent exotropia is the most common type of strabismus It is defined as a nonconstant exodeviation that manifests predominantly at distance fixation and may progress over a variable period to near fixation This entity is also named distance exotropia, divergent squint, periodic exotropia, or exotropia of inattention Small exophorias are common in newborns and can beExodeviation is a horizontal form of strabismus characterized by visual axes that form a divergent angle The different types of acquired exotropia are intermittent exotropia, sensory exotropia,Introduction Primary exotropia is a divergent strabismus that appears from the first day of life to the second year It can be isolated or associated with a pathological context requiring cerebral imaging to determine diagnosis and prognosis




Strabismus




Squint Dr Abdulrhman Alsagaihi Ppt Download
Exotropia causes There is no specific, known cause of exotropia However, exotropia may be common in children with either sensory exotropia or an underlying genetic disorder that impacts eye movements Here is a list of some diseases that could increase the likelihood of developing exotropia In the case of sensory exotropia, the poor acuity of one eye is the cause of theCommonly referred to as crossed eyes, esotropia is a common type of strabismus in which one or both eyes turn inward toward the nose It is most often identified in children between the ages of 2 and 4, although it can occur at any age The opposite of esotropia is exotropia, which is characterized byI have a major astigmatism in both eyes, alternating strabismus with exotropia in the left eye (575 vision) and in the right eye, amblyopia (vision >2/400), and it turns in Photophobia Treatment If you're suffering from photophobia that has begun recently, it may be linked to causes other than a functional vision problem



Accommodative Esotropia Dr Francis Dube Optometrist




Syah S Optometry Blog Exotropia Classification
Types of exotropia Congenital exotropia Congenital exotropia is also called infantile exotropia People with this condition have an Sensory exotropia Poor vision in the eye causes it to turn outward and not work in tandem with the straight eye This Acquired exotropia This type of exotropiaIntermittent exotropia In this type of strabismus, one eye will fixate (concentrate) on a target while the other eye is pointing outward Symptoms may include double vision, headaches, difficulty reading, eyestrain, and closing one eye when viewing far away objects or when in bright lightThe underlying cause of exophoria isn't clearly known However, the primary issue of exophoria is a weakness in the eye muscles This muscle weakness causes




Intermittent Distance Exotropia Hull University Teaching Hospitals Nhs Trust




Strabismus Prof Dr Emel Baar Cerrahpaa Tp Fakltesi
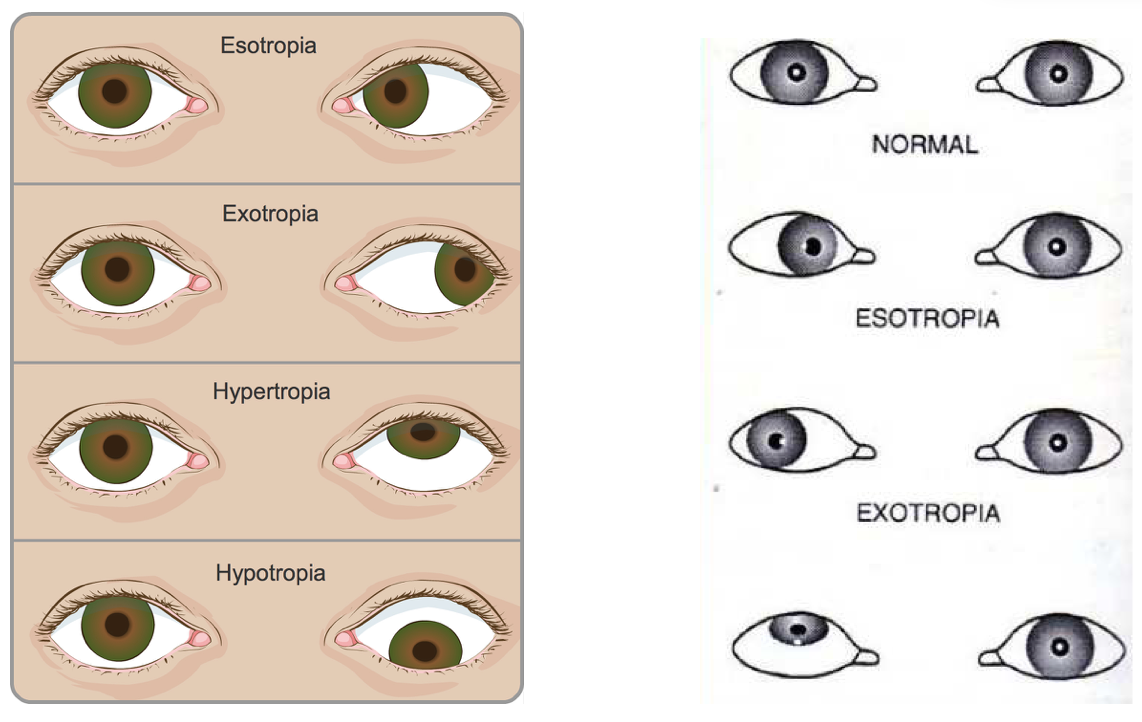
Manifest intermittent exotropia may increase with time and become constant exotropia Sensory deprivation exotropia Sensory deprivation exotropia is due to disruption of binocular reflexes by acquired conditions like opaque media due to a disease or cataract It begins in children over five years of age or in adultsMechanical Exotropia Mechanical exotropia is often due to fibrosis (or scar tissue) that prevents the eye from moving inward Some conditions, such as overactive thyroid, can leave deposits in muscles and cause an abnormal tightness for an eye muscle to moveWhat is Exotropia Exotropia, a form of Strabismus, is the outward deviation (turn) of an eye and occurs in 12% of children by 7 years of age and occurs equally in males and femalesIn exotropia, one or both eyes turn out What are the symptoms The




Pdf Consecutive Exotropia A Case Report And Review Of Literature




Management Of Intermittent Exotropia Of The Divergence Excess Type A Teaching Case Report The Journal Of Optometric Education
Headaches, or abnormal head posture Although the exact cause cannot This Optometric Clinical Practice Guideline for the Care of the Patient with Strabismus describes appropriate examination, diagnosis, treatment, and management to reduce the risk of visual disability from esotropia and exotropia through timely care This Guideline will assistExotropia is a type of strabismus (misaligned eyes) in which one or both of the eyes turn outward The condition can begin as early as the first few months of life or any time during childhood Exotropia often begins as an intermittent problem, noticed only when the child is tired, sick, just waking up, excited, or stressedIn Exotropia the Eyes are deviated outwards It causes Double Vision and tiredness in the Eyes It is associated with Squint and Strabismus There are three types of Exotropia Congenital Strabismus It is present by birth It may be due to genetic disorders Intermittent Exotropia It may be seen in day dreaming



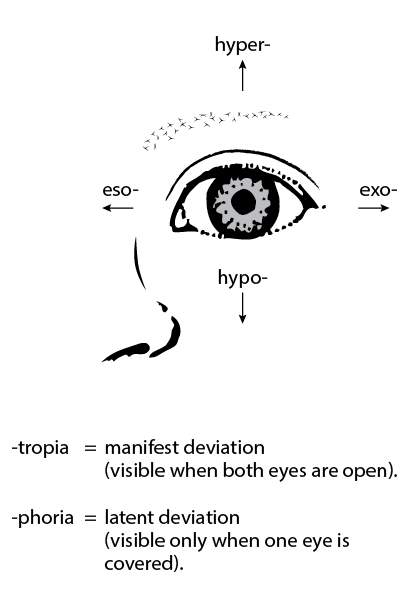
Esophoria
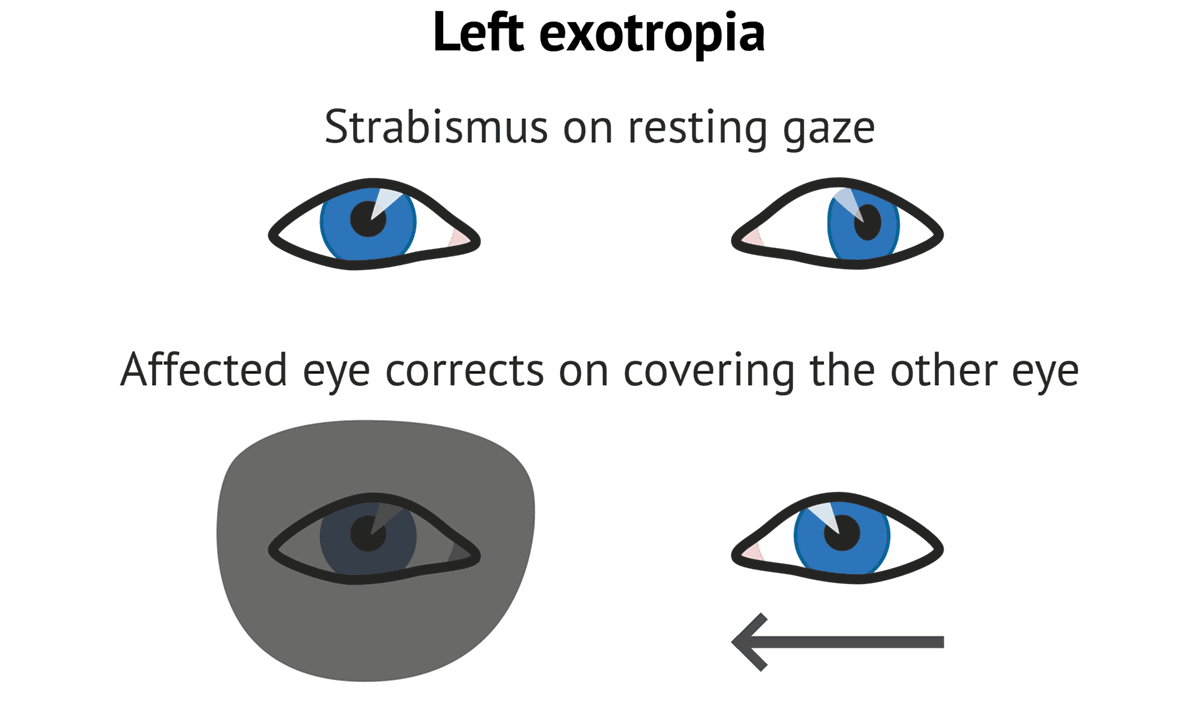



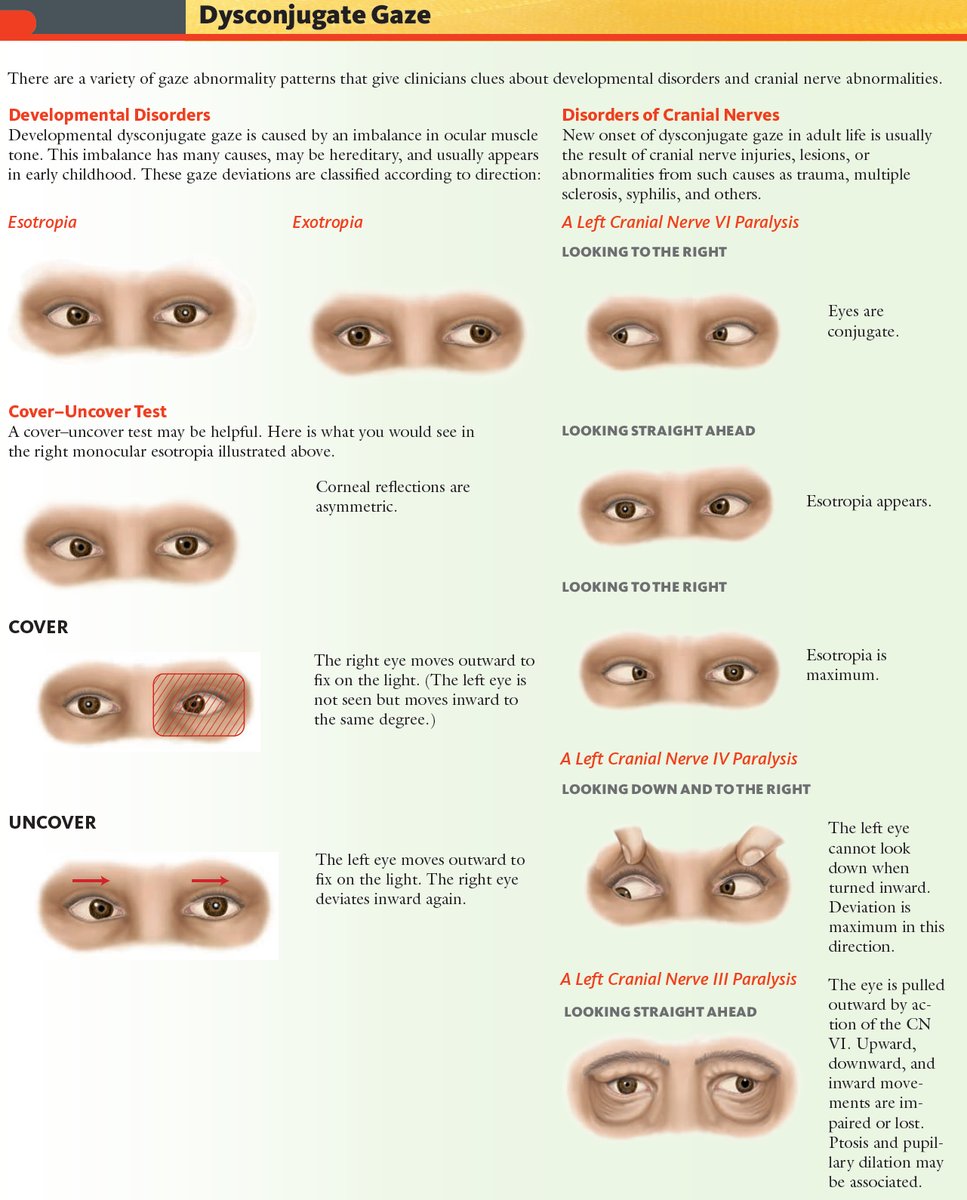
Strabismus Cranial Nerves Medschool
The etiology of intermittent exotropia is largely unknown, 5 and the deviating movement shares features with normal divergent eye movements, but divergence tone may exceed convergence tone in these patients, correlating with hypometric adduction saccades 6,7Sensory exotropia accounts for 25% of all causes of acquired exotropias The deviation angles are characteristically large An eye with longstanding sensory exotropia often develops any of the several mechanical and innervational abnormalities, especially if the angle isCauses Exotropia occurs when there is an imbalance in the eye muscles or when there is a signaling problem between the brain and the eye Sometimes a health problem, such as cataracts or a stroke, can cause this to occur The condition can also be inherited
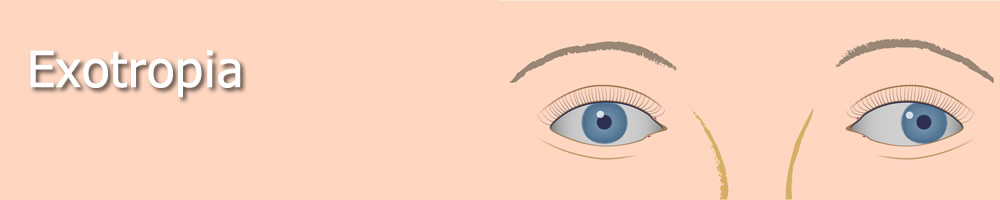



Exotropia Outward Eye Turn




Strabismus Natural Ways To Help Resolve Crossed Eyes Dr Axe
The cause of this condition is not known Most experts believe that the brain of affected patients has trouble controlling the position of the eye Signs and symptoms of intermittent exotropia Abnormal outward movement of the eye happens most often when the child is focusing on distant targets, such as watching televisionExotropia or exoforia Exotropia is a defect that occurs when the eyes are turned outward, which causes a major blurred vision problemExophoria is a type of strabismus and is also known colloquially as wall eyes The exophoria can be congenital o acquired and it is more common in women than in menCauses of esotropia and exotropia are mostly unknown Children with a family history of the disorder are more likely to get them They are also common in children who have other systemic (chromosomal or neurologic) disorders No known cause




Strabismus Amblyopia Leukocoria Ppt Video Online Download
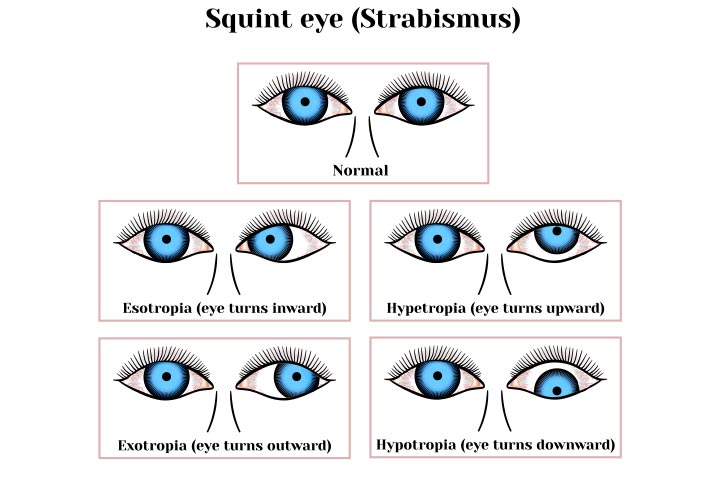



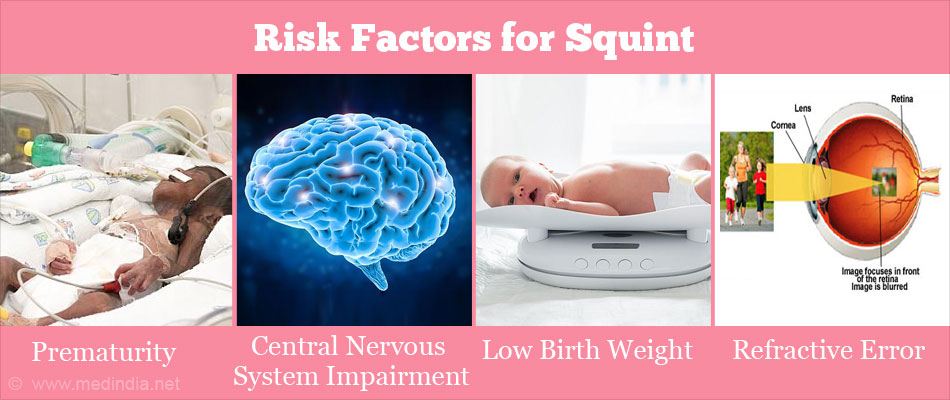
Strabismus In Infants Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Risks
Exotropia can cause complications, including Headaches Trouble reading EyestrainBut when there is a disruption and the muscles do not work together, some form of strabismus, including exotropia, may occur Other causes may involve the nerves that transmit information from the brain to the muscles, or the part of the brain that directs eye movementsConstant exotropia may be congenital, but poor vision in the outwardturning eye is also a cause Diagnosis Exotropia is an indication to examine the eye for intraocular disease Management In children with intermittent exotropia, the decision to perform corrective surgery depends on the frequency and degree of the abnormality When exotropia



Strabismus For The Anterior Segment Surgeon Sensory Exotropia




Amblyopia In Vienna Lazy Eye In Vienna Vienna Lazy Eye
Some people have exotropia from childhood, called a "lazy eye" Others develop it as an adult due to a medical condition like a stroke or thyroid disease Others develop it as an adult when one eye loses vision The eye with poor vision can wander How is



Amblyopia Guide Causes Treatment More Nvision Eye Centers




Signs And Symptoms Of Binocular Vision Problems




Exotropia Psychology Wiki Fandom



Management Of Squint With Near Distance Angle Disparity Eye News




Eye And Vision Issues In Noonan Syndrome Noonan Syndrome Awareness Association



Nystagmus
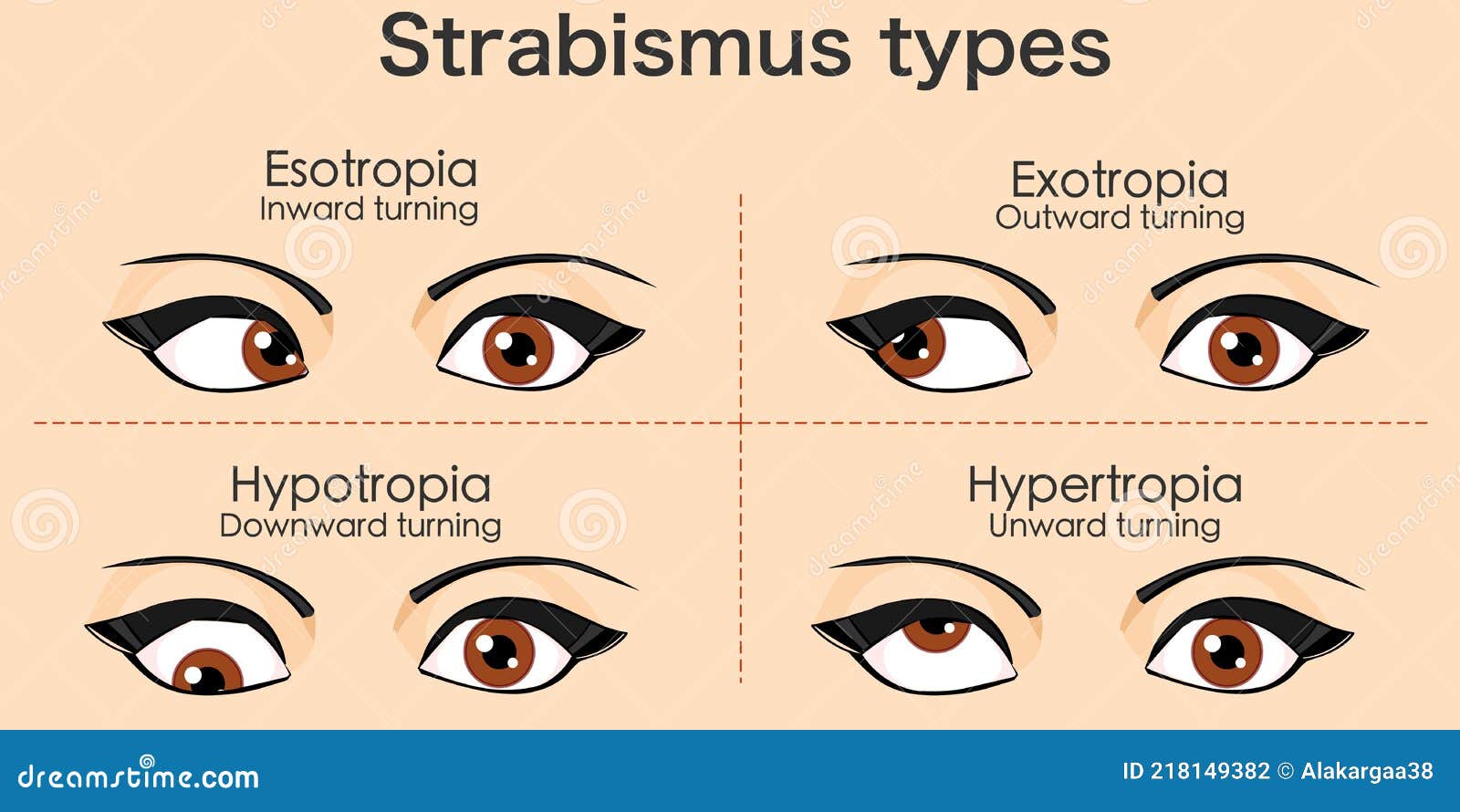



Exotropia Stock Illustrations 50 Exotropia Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Exophoria




Do You See A Pattern




What Is Accommodative Esotropia




Strabismus Amblyopia Leukocoria Saeed Alwadani Md Assistant Professor




Strabismus Ocular Misalignment Differential Diagnosis Grepmed



Concomitant Strabismus Springerlink




Strabismus



1




Prevalence Of Sagging Eye Syndrome In Adults With Binocular Diplopia Ento Key



Dysconjugate Gaze Esotropia Exotropia And Cranial Grepmed



Strabismus Baby Symptoms Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis




8 Intermittent Exotropia Ideas Strabismus Surgery Vision Therapy Eye Surgery



Esotropia Everyday Sight




Strabismus Surgery For Misaligned Eyes Crossed Eyes Or Wall Eyes




Exodeviations An Exodeviation Is A Divergent Strabismus That




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




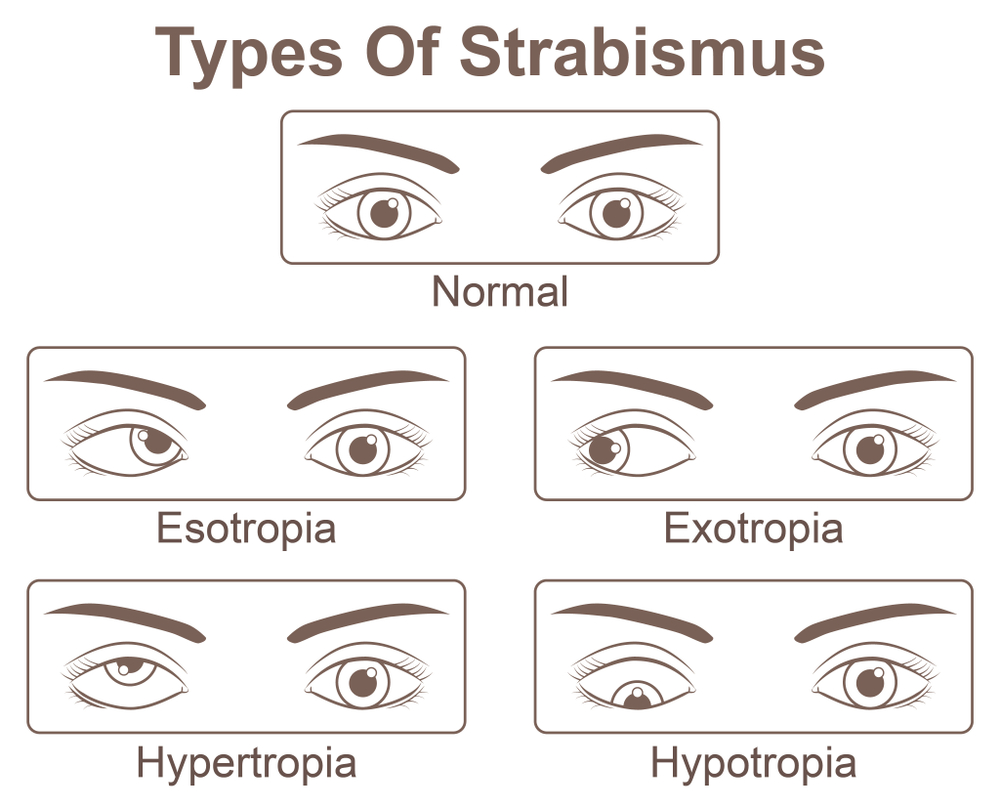
Types Of Strabismus Stock Vector Illustration Of Diagnosis



Strabismus Pediatrics Msd Manual Professional Edition
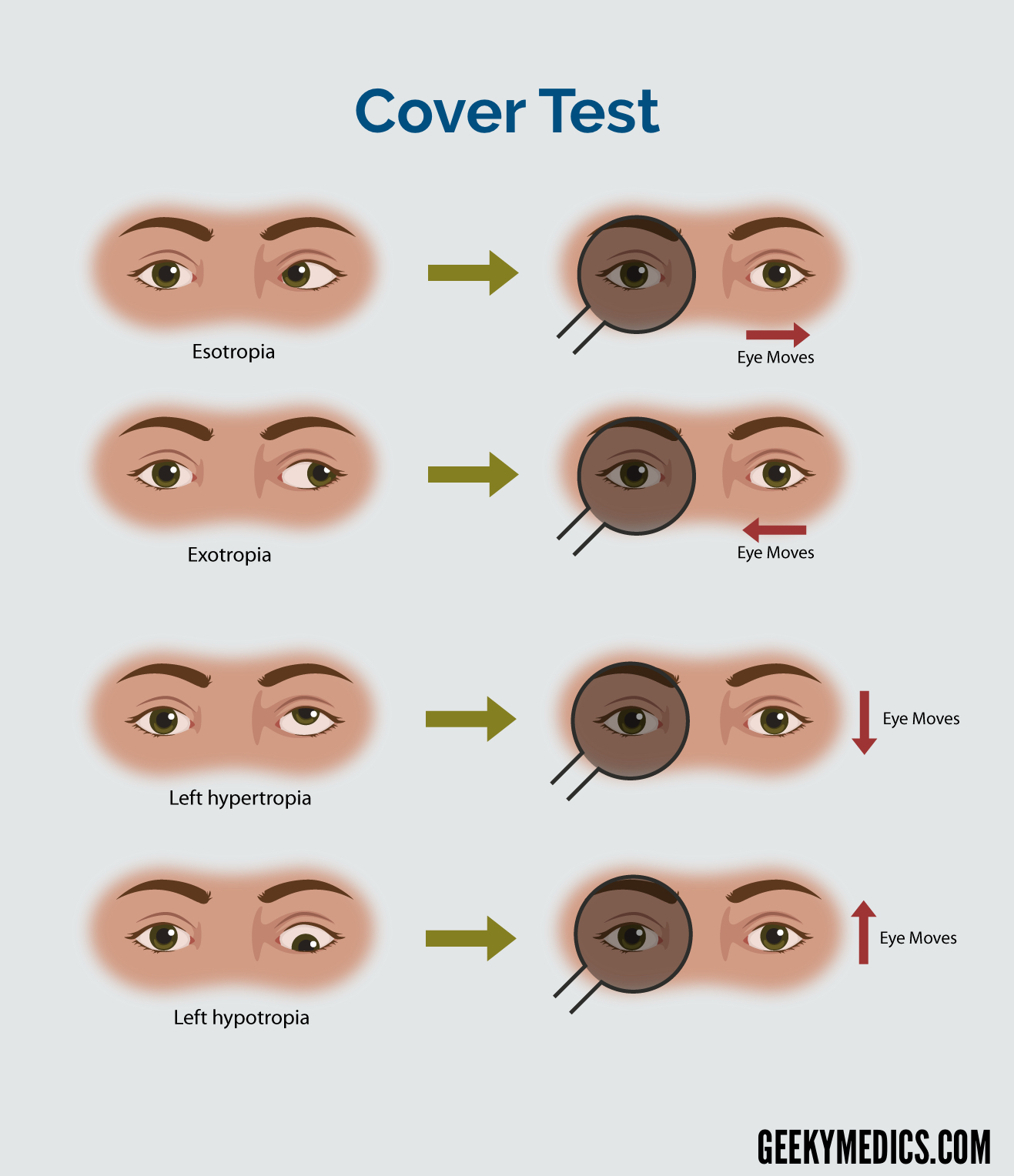



Strabismus Exotropia Esotropia Cover Test Geeky Medics
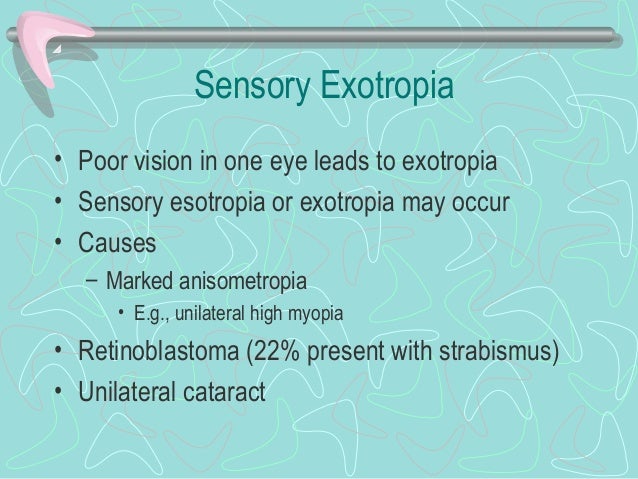



13 Exotropia




Strabismus American Association For Pediatric Ophthalmology And Strabismus




Assessing Strabismus In Children Paediatrics And Child Health




How To Fix Cross Eyes Naturally Image Optometry



Acquired Exotropia Clinical Presentation History Physical Causes
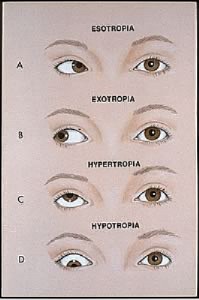



Strabismus Dr Vryghem



Strabismus Cranial Nerves Medschool



Exotropia Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention




Axial Mri In A Normal Control And A Subject With Exotropia Imaged In Download Scientific Diagram




Strabismus Pediatrics Msd Manual Professional Edition




Gulf View Medical Centre Exotropia Misalignment Of The Eyes Learn More About The Symptoms Causes Complications Treatment What Is Exotropia Exotropia Is A Type Of Strabismus Which Is A




Strabismus Amblyopia Leukocoria Dr Hessah Alodan Pediatric Opthalmology




Exophoria Definition Treatment And How It Compares To Exotropia




My Eyes Are Moving On Their Own Involuntarily One Eye




How To Treat Crossed Eyes Strabismus Vision Eye Eye Exercises Eye Health




Exophoria Aetiology Youtube



What Is Amblyopia New Horizons Vision Therapy




Exotropia Eyewiki




Strabismus Lazy Eye Mckenzie Pediatrics




Strabismus Dra Fernandez Agrafojo




Esotropia Made Simple For The Postgraduates



1




Squint




Ocular Motility Disorders And Strabismus Knowledge Amboss



What Is Strabismus The Optometry Center For Vision Therapy



Strabismus Ananthaksha Super Speciality Eye Hospital



Strabismus Squint Singapore Causes Treatment Options




Exotropia Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention




Consecutive Exotropia Ppt Download




Kampala Lasik Center What Causes Strabismus Squint Strabismus Occurs When There Are Neurological Or Anatomical Problems That Interfere With The Control And Function Of The Extraocular Muscles The Problem May




What Is Strabismus Causes Symptoms Treatment




All About Strabismus Eye Center Of Northern Colorado Eye Center Of Northern Colorado




13 Exotropia




Exophoria




Strabismus Omar Abughanimeh Seminar Content Introduction Definition Causes




Strabismus



Squint Sunetram Eye Care




Diplopia Dr Mohammed Alanazy Versions Terminology Esotropia Exotropia




Exotropia American Association For Pediatric Ophthalmology And Strabismus




Exotropia



Pattern Strabismus American Academy Of Ophthalmology
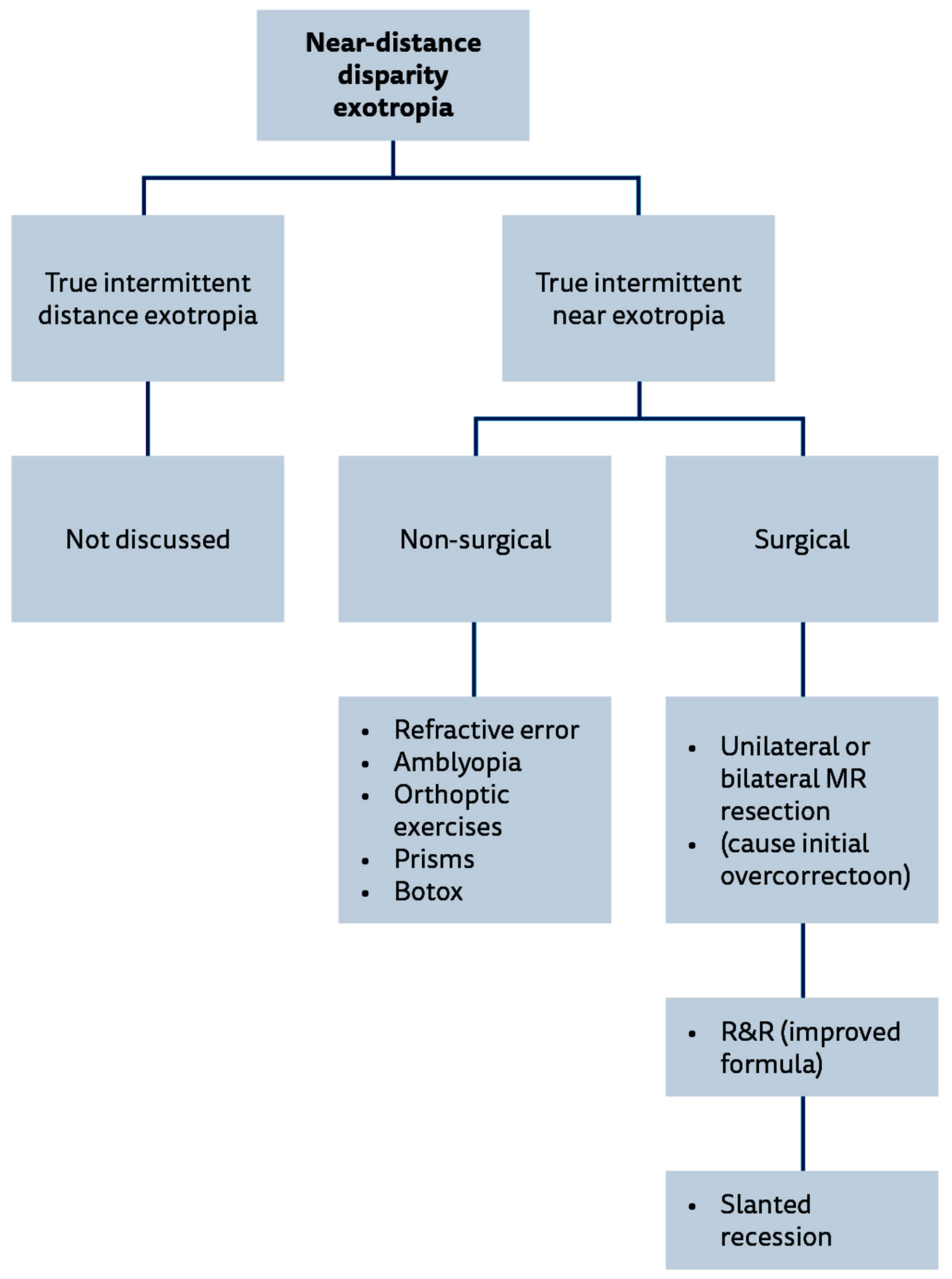



Management Of Squint With Near Distance Angle Disparity Eye News




What Is Exotropia Causes Symptoms Treatment Prognosis Complications




Amblyopia What It Is What Causes It How To Treat It




Esotropia Crossed Eyes Lazy Eye Or Squint Pediatric Ophthalmology Pa
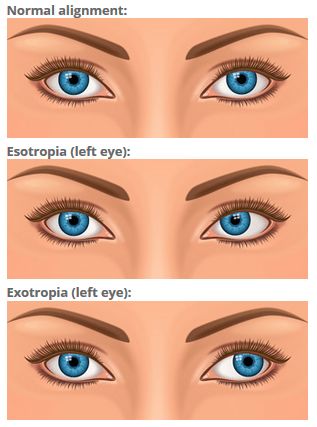



Strabismus And Crossed Eyes Causes And Treatment All About Vision




Exotropia Symptoms Management And More




What Is Strabismus Causes Symptoms Treatment
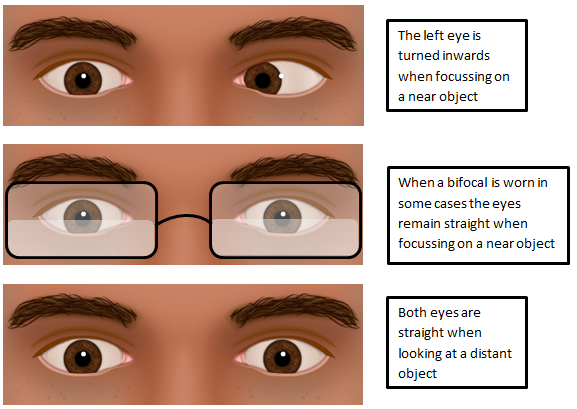



Convergence Excess Type Intermittent Esotropia Hull University Teaching Hospitals Nhs Trust
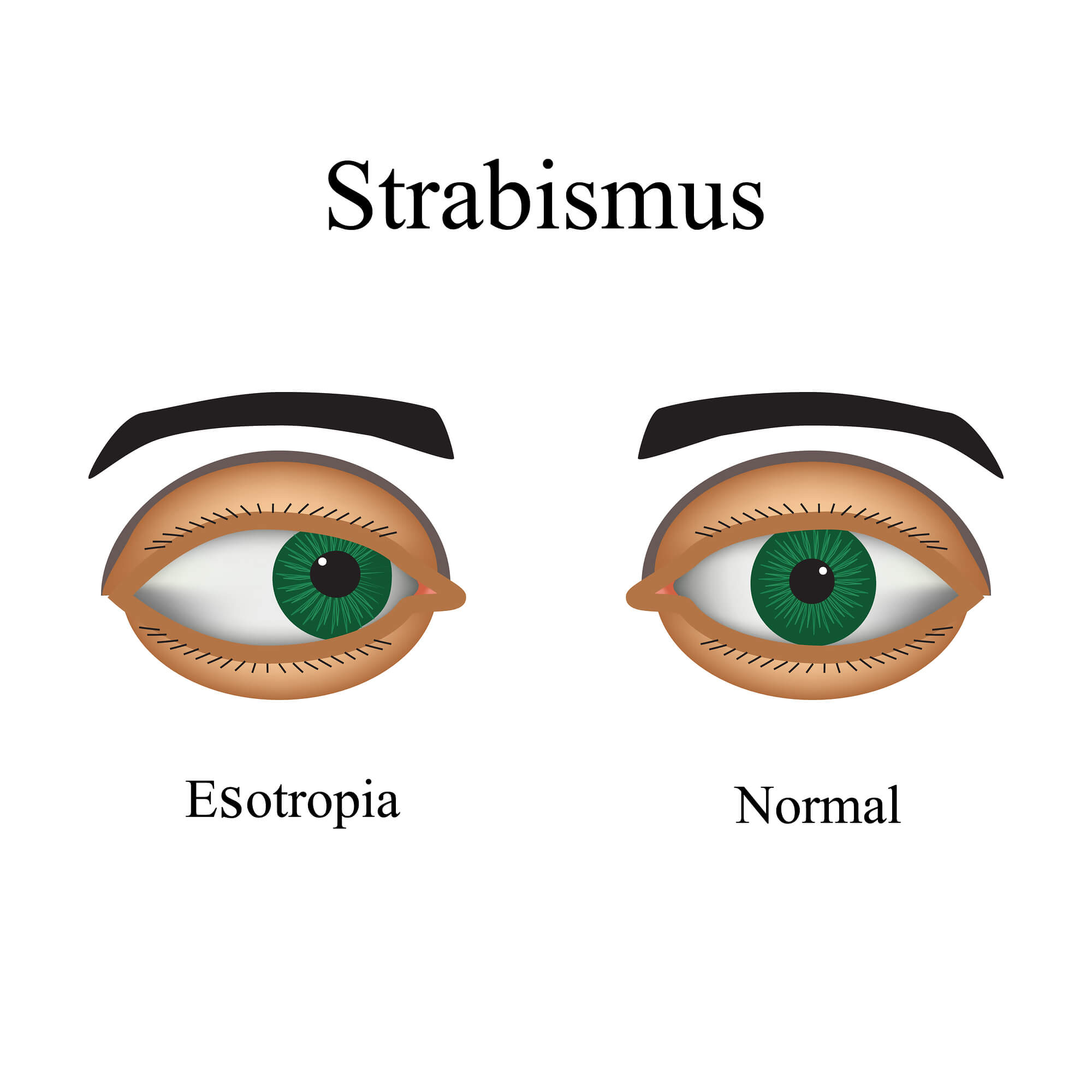



All About Crossed Eyes And Lazy Eye




Exotropia Divergent Squint
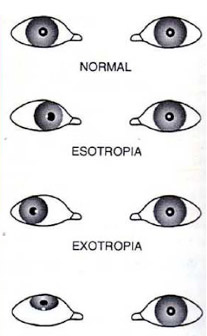



Treatment For Squint In Child Singapore Causes Complications




Management Of Intermittent Exotropia Of The Divergence Excess Type A Teaching Case Report The Journal Of Optometric Education




Crossed Eyes Strabismus Squint Misaligned Eyes Dr Ali A Taqi Ppt Video Online Download
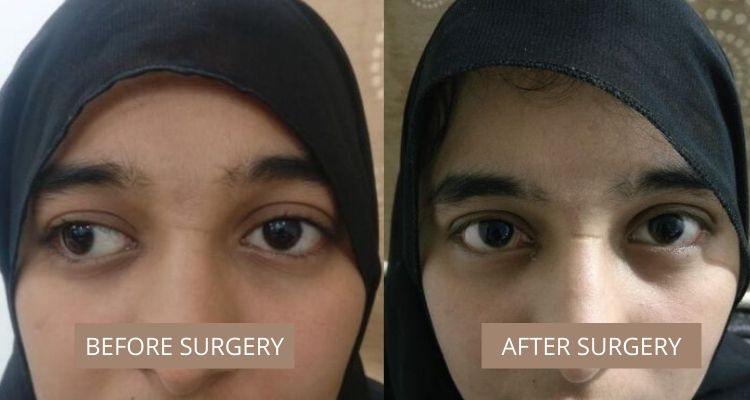



Exotropia Best Squint Treatment In Mumbai Eye Solutions




Exotropia Eyes Turn Outward Causes Symptoms Treatment Vision Center



What Is Exotropia Vision Express




Hypertropia Explore Facebook
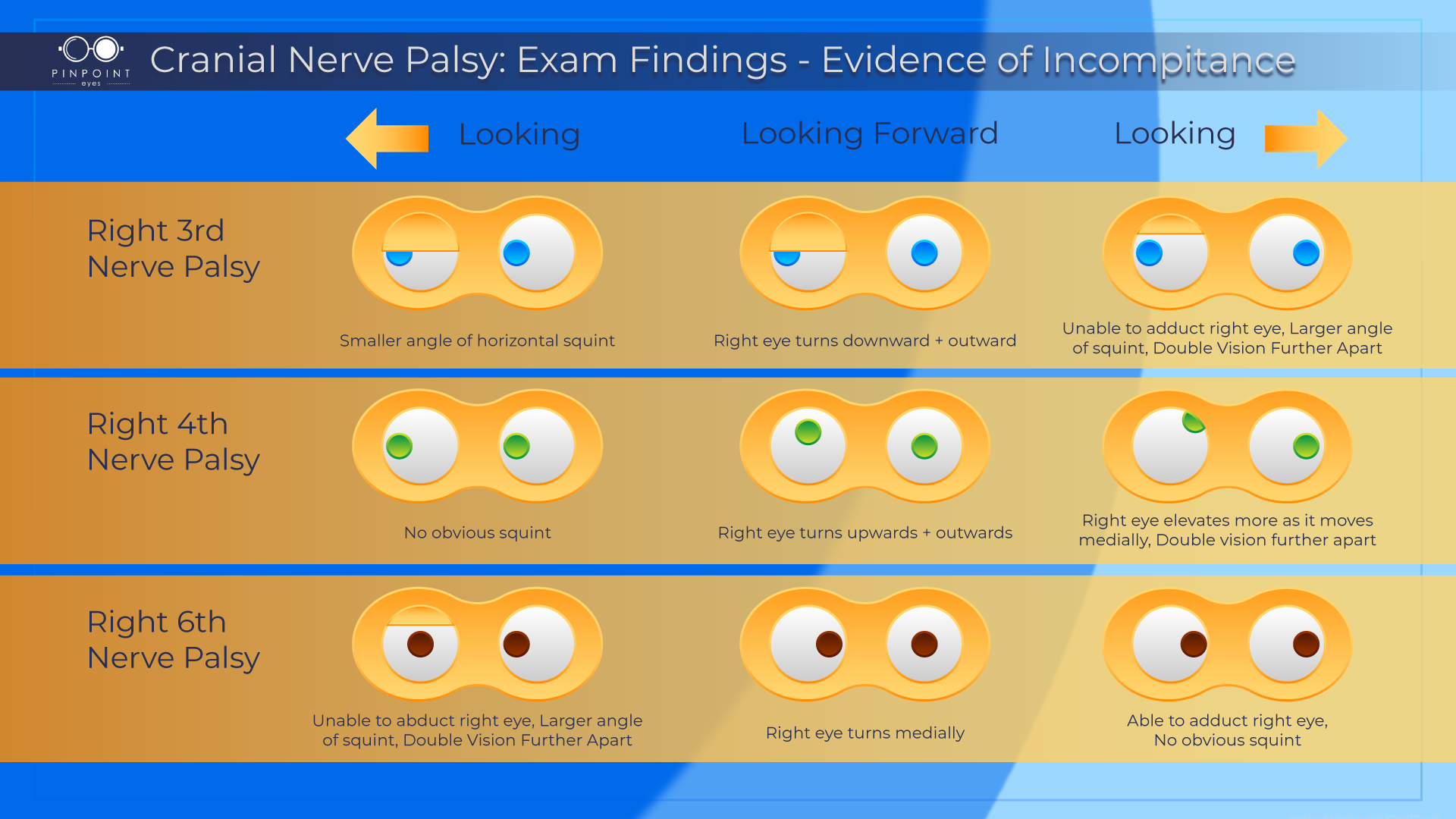



Causes For Strabismus Cranial Nerve Palsy Pinpointeyes




Capella Eyecare Exotropia Strabismus Is A Condition In Which One Eye Is Looking Straight And The Other Eye Is Turned Inward Outward Upward Downward As You Can See From This Photo



V Patterns Esotropia And Exotropia And Their Management By Dr Sudhir Singh




Strabismus Causes And Treatments



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿